-
 Natural and Designed Cyclic Peptides as Potential Antiviral Drugs to Combat Future Coronavirus Outbreaks
Natural and Designed Cyclic Peptides as Potential Antiviral Drugs to Combat Future Coronavirus Outbreaks -
 Heavy Metals in Particulate Matter—Trends and Impacts on Environment
Heavy Metals in Particulate Matter—Trends and Impacts on Environment -
 Protein O-Fucosyltransferases: Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms in Mammals
Protein O-Fucosyltransferases: Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms in Mammals -
 Theoretical Insights into the Impact of Pyrrole and Imidazole Substituents on the BODIPY Chromophore
Theoretical Insights into the Impact of Pyrrole and Imidazole Substituents on the BODIPY Chromophore
Journal Description
Molecules
Molecules
is the leading international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of chemistry. Molecules is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The International Society of Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids (IS3NA), the Spanish Society of Medicinal Chemistry (SEQT) and the International Society of Heterocyclic Chemistry (ISHC) are affiliated with Molecules and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Reaxys, CaPlus / SciFinder, MarinLit, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biochemistry and Molecular Biology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Organic Chemistry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 25 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Molecules.
- Companion journal: Foundations.
- Journal Cluster of Chemical Reactions and Catalysis: Catalysts, Chemistry, Electrochem, Inorganics, Molecules, Organics, Oxygen, Photochem, Reactions, Sustainable Chemistry.
Impact Factor:
4.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
The Potential Anti-Cancer Effects of Polish Ethanolic Extract of Propolis and Quercetin on Glioma Cells Under Hypoxic Conditions
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3008; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143008 (registering DOI) - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Tissue hypoxia is commonly observed in head cancers and contributes to both molecular and functional changes in tumour cells. It is known to stimulate erythropoiesis, angiogenesis, and metabolic alterations within tumour cells. Glioblastoma, a type of brain tumour, is characterized by rapid proliferation
[...] Read more.
Tissue hypoxia is commonly observed in head cancers and contributes to both molecular and functional changes in tumour cells. It is known to stimulate erythropoiesis, angiogenesis, and metabolic alterations within tumour cells. Glioblastoma, a type of brain tumour, is characterized by rapid proliferation and aggressive growth. Recent studies have indicated that natural products may hold potential as components of cancer therapy. Among these, Polish propolis and its active compound, quercetin, have demonstrated promising anti-cancer properties. The aim of this study was to evaluate the concentrations of selected cytokines—specifically IL-6, IL-9, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-BB), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)—produced by astrocytes of the CCF-STTG1 cell line. The cytotoxic effects of ethanolic extract of propolis (EEP) and quercetin were assessed using the MTT assay. Astrocytes were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 200 ng/mL) and/or IFN-α (100 U/mL), followed by treatment with EEP or quercetin (25–50 µg/mL) under hypoxic conditions for two hours. Cytokine concentrations were measured using the xMAP Luminex Multiplex Immunoassay and the Multiplex Bead-Based Cytokine Kit. Our study demonstrated that Polish propolis and its component quercetin modulate the tumour microenvironment in vitro, primarily by altering the levels of specific cytokines. The HCA analysis revealed that IL-6 and MCP-1 formed a distinct cluster at the highest linkage distance (approximately 100% of Dmax), suggesting that their expression patterns are significantly different from those of the other cytokines and that they are more similar to each other than to the rest. PCA analysis showed that EEP-PL (50 μg/mL) with IFN-α and EEP-PL (50 μg/mL) with LPS exert similar activities on cytokine secretion by astrocytes. Similar effects were demonstrated for EEP-PL 50 μg/mL + LPS + IFN-α, EEP-PL 25 μg/mL + IFN-α and EEP-PL 25 μg/mL + LPS + IFN-α. Our findings suggest that Polish propolis and quercetin may serve as promising natural agents to support the treatment of stage IV malignant astrocytoma. Nonetheless, further research is needed to confirm these results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioactive Compounds and Small Molecules with Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Functions)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Reversible Binding of Nitric Oxide in a Cu(II)-Containing Microporous Metal-Organic Framework
by
Konstantin A. Bikov, Götz Schuck and Peter A. Georgiev
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3007; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143007 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
We studied the adsorption thermodynamics and mechanism behind the binding of nitric oxide (NO) in the interior surfaces and structural fragments of the high metal center density microporous Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) CPO-27-Cu, by gas sorption, at a series of temperatures. For the purpose
[...] Read more.
We studied the adsorption thermodynamics and mechanism behind the binding of nitric oxide (NO) in the interior surfaces and structural fragments of the high metal center density microporous Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) CPO-27-Cu, by gas sorption, at a series of temperatures. For the purpose of comparison, we also measured the corresponding CO2 adsorption isotherms, and as a result, the isosteric heats of adsorption for the two studied adsorptives were derived, being in the range of 12–15 kJ/mol for NO at loadings up to 0.5 NO molecules per formula unit (f.u.) of the bare compound (C4O3HCu), and 23–25 kJ/mol CO2 in the range 0–1 CO2 per f.u. Microscopically, the mode of NO binding near the square pyramid Cu(II) centers was directly accessed with the use of in situ NO gas adsorption X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS). Additionally, during the vacuum/temperature activation of the material and consequent NO adsorption, the electronic state of the Cu-species was monitored by observing the corresponding X-ray Near Edge Spectra (XANES). Contrary to the previously anticipated chemisorption mechanism for NO binding at Cu(II) species, we found that at slightly elevated temperatures, under ambient, but also cryogenic conditions, only relatively weak physisorption takes place, with no evidence for a particular adsorption preference to the coordinatively unsaturated Cu-centers of the material.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Functional Porous Frameworks: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications)
Open AccessArticle
NaDES-Based Extracts by Microwave Activation from Laurus nobilis L. Leaves: Sustainable Multifunctional Ingredients for Potential Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Applications
by
Debora Caviglia, Eleonora Russo, Anna Maria Schito, Francesco Saverio Robustelli della Cuna, Elena Grignani, Nicola Lionetti and Carla Villa
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3006; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143006 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Laurus nobilis L. is a widely cultivated plant, used for ornamental purposes, as a high-value spice crop, and in the flavor and fragrance industry. In natural medicine, it is well-known for its many beneficial properties (due to a broad spectrum of biologically active
[...] Read more.
Laurus nobilis L. is a widely cultivated plant, used for ornamental purposes, as a high-value spice crop, and in the flavor and fragrance industry. In natural medicine, it is well-known for its many beneficial properties (due to a broad spectrum of biologically active compounds) and used for the treatment of different disorders. In this study, natural deep eutectic solvents (NaDESs), coupled with microwave activation, were studied and applied for a green extraction of L. nobilis leaves. The main objective was to obtain a sustainable and multifunctional cosmetic and pharmaceutical ingredient (the NaDES-based extract itself), exploiting both the intrinsic cosmetic functionalities of NaDES components and the biological properties of laurel bioactive compounds. The most promising candidate was obtained from a eutectic system containing betaine, glycerol, and lactic acid. The evaluation of this NaDES-based complex reveals a considerable number of phenolic compounds (around 11.57 mg of gallic acid equivalents for a gram of fresh leaves) and a notable antioxidant activity (80.1% with respect to Trolox), with values quite constant over a period of six months. The complex exhibits effective antimicrobial activity against different Gram-positive (S. aureus and S. epidermidis) and Gram-negative (E. coli and P. aeruginosa) bacterial strains, with concentrations ranging from 3.8 to 7.5 mg/mL. Furthermore, the extract presents a pleasant fragrance, attributable to the selective extraction of different volatile aromatic compounds, as confirmed by GC-MS analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovation in Green Extraction and Processing—a Themed Issue in Memory of Professor Farid Chemat for His Outstanding Contributions to Green Chemistry (1968–2023))
►▼
Show Figures
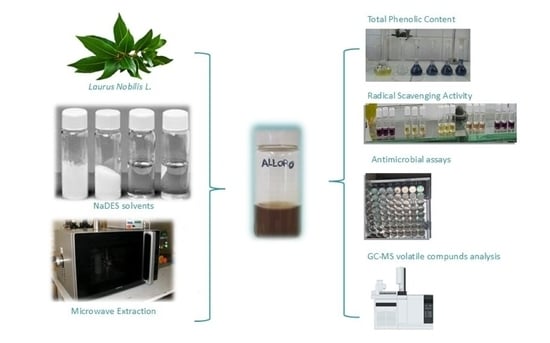
Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Ketone-Assisted Alkoxysilane Condensation to Form Siloxane Bonds
by
Sławomir Rubinsztajn, Marek Cypryk, Jan Kurjata, Małgorzata Kwiatkowska and Urszula Mizerska
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3005; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143005 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Siloxane bond formation represents a fundamental reaction central to both silicone chemistry and its technological applications. This paper presents a novel ketone-assisted process for the condensation of alkoxy-functional silanes catalyzed by a cationic Ge(II) complex stabilized by pentamethylcyclopentadiene Cp*Ge(II)+. This process
[...] Read more.
Siloxane bond formation represents a fundamental reaction central to both silicone chemistry and its technological applications. This paper presents a novel ketone-assisted process for the condensation of alkoxy-functional silanes catalyzed by a cationic Ge(II) complex stabilized by pentamethylcyclopentadiene Cp*Ge(II)+. This process leads to the formation of siloxane bonds, with dialkoxy ketal as a byproduct. Unlike the analogous reaction involving aldehydes, the ketone-assisted process is reversible, resulting in the formation of a mixture of alkoxy-functionalized silane or siloxane, along with the corresponding disiloxane product. Additionally, the introduced ketone underwent only partial conversion to the corresponding ketal. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that the siloxane bond could be cleaved to form alkoxysilane in the presence of the ketal and a cationic Cp*Ge(II) complex acting as a catalyst.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Macromolecular Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
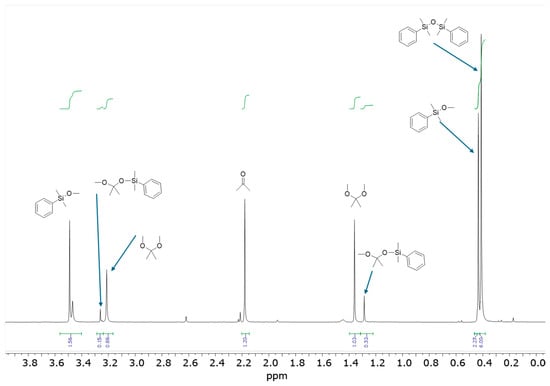
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis of Substituted 1,4-Benzodiazepines by Palladium-Catalyzed Cyclization of N-Tosyl-Disubstituted 2-Aminobenzylamines with Propargylic Carbonates
by
Masahiro Yoshida, Saya Okubo, Akira Kurosaka, Shunya Mori, Touya Kariya and Kenji Matsumoto
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3004; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143004 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
A synthesis of substituted 1,4-benzodiazepines has been developed via palladium-catalyzed cyclization of N-tosyl-disubstituted 2-aminobenzylamines with propargylic carbonates. The reaction proceeds through the formation of π-allylpalladium intermediates, which undergo intramolecular nucleophilic attack by the amide nitrogen to afford seven-membered benzodiazepine cores. In reactions
[...] Read more.
A synthesis of substituted 1,4-benzodiazepines has been developed via palladium-catalyzed cyclization of N-tosyl-disubstituted 2-aminobenzylamines with propargylic carbonates. The reaction proceeds through the formation of π-allylpalladium intermediates, which undergo intramolecular nucleophilic attack by the amide nitrogen to afford seven-membered benzodiazepine cores. In reactions involving unsymmetrical diaryl-substituted carbonates, regioselectivity was observed to favor nucleophilic attack at the alkyne terminus substituted with the more electron-rich aryl group, suggesting that electronic effects play a key role in determining product distribution. The versatility of this reaction was further demonstrated by constructing a benzodiazepine framework found in bioactive molecules, indicating its potential utility in medicinal chemistry. Mechanistic insights supported by stereochemical outcomes and X-ray crystallographic analysis of key intermediates reinforce the proposed reaction pathway. This palladium-catalyzed protocol thus offers an efficient and practical approach to access structurally diverse benzodiazepine derivatives.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Heterocyclic Synthesis, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
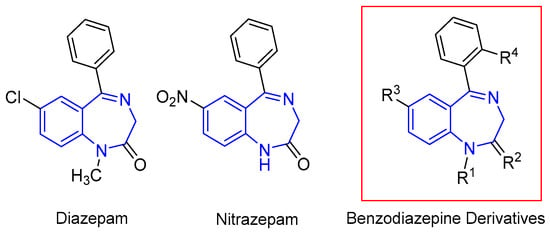
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Noncovalently Immobilized Glucose Oxidase/Horseradish Peroxidase Cascade on Polyamide Supports for Eco-Friendly Polyaniline Synthesis
by
Nadya V. Dencheva, Joana F. Braz, Sofia A. Guimarães and Zlatan Z. Denchev
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3003; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143003 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
This study discloses the noncovalent immobilization of a bienzyme cascade composed of glucose oxidase (GOx) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) onto magnetically responsive polyamide microparticles (PA MPs). Porous PA6, PA4, and PA12 MPs containing iron fillers were synthesized via activated anionic ring-opening polymerization in
[...] Read more.
This study discloses the noncovalent immobilization of a bienzyme cascade composed of glucose oxidase (GOx) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) onto magnetically responsive polyamide microparticles (PA MPs). Porous PA6, PA4, and PA12 MPs containing iron fillers were synthesized via activated anionic ring-opening polymerization in suspension, alongside neat PA6 MPs used as a reference. Four hybrid catalytic systems (GOx/HRP@PA) were prepared through sequential adsorption of HRP and GOx onto the various PA MP supports. The initial morphologies of the supports and the hybrid biocatalysts were characterized by SEM, followed by evaluation of the catalytic performance using a two-step glucose oxidation cascade process. Among all systems, the GOx/HRP@PA4-Fe complex exhibited the highest activity, being approximately 1.5 times greater than the native enzyme dyad, followed by the PA6-supported system with slightly inferior performance. All systems obeyed Michaelis–Menten kinetics, with the immobilized cascades displaying higher Kₘ and Vₘₐₓ values than the non-immobilized enzyme pair while maintaining comparable catalytic efficiencies, CE (CE = kcat/Kₘ). Subsequently, the immobilized and native enzyme systems were employed for the polymerization of aniline. According to UV–VIS, complete monomer conversion was achieved within 24 h for selected catalysts, and FTIR analysis confirmed the formation of polyaniline in the emeraldine base form without the use of template molecules. These findings highlight the potential of Fe-containing polyamide microparticles as efficient supports for the sustainable, enzyme-mediated synthesis of intrinsically conductive aromatic polymers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Polymer-Based Materials, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Varietal Susceptibility of Yellow Onions to Blanching and Its Impact on Probiotic Fermentation
by
Katarzyna Grzelak-Błaszczyk, Robert Klewicki, Sylwia Ścieszka, Lidia Piekarska-Radzik, Michał Sójka, Michalina Jaszczak, Elżbieta Klewicka, Bartosz Fotschki and Jerzy Juśkiewicz
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3002; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143002 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The purpose of this study was to determine the impact of blanching various onion (Allium cepa L.) varieties on the process of lactic fermentation by probiotic strain Levilactobacillus brevis ŁOCK 0944. The materials for the research were twelve varieties of yellow onion: Venecia,
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this study was to determine the impact of blanching various onion (Allium cepa L.) varieties on the process of lactic fermentation by probiotic strain Levilactobacillus brevis ŁOCK 0944. The materials for the research were twelve varieties of yellow onion: Venecia, Moondance, Sedona, Alonso, Hysky, Centro, Dormo, Hypark, Hybelle, Armstrong, EXP 2236, and Hysinger. We also studied the resulting changes in bioactive compound content. Acidic bacterial metabolites, the lactic acid bacteria count, and the polyphenol and carbohydrate contents were assessed in both raw onions and onions blanched at 60 °C, before and after fermentation. Onion varieties that showed morphological changes after blanching (Hysky, Centro, Dormo) demonstrated better growth of L. brevis and higher lactic acid production. Blanching loosened the tissue structure, reducing the carbohydrate content in the blanched and fermented onions, particularly Alonso, Centro, Dormo, and Hypark varieties. Although the combined process reduced the polyphenol content, four varieties showed no statistically significant differences, indicating variety-specific responses. The varying susceptibility of onion varieties to thermal treatment highlights the importance of selecting the appropriate variety for further processing.
Full article

Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Mass Spectrometric Fingerprinting to Detect Fraud and Herbal Adulteration in Plant Food Supplements
by
Surbhi Ranjan, Tanika Van Mulders, Koen De Cremer, Erwin Adams and Eric Deconinck
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3001; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143001 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Mass spectrometric (MS) fingerprinting coupled with chemometrics for the detection of plants in plant mixtures is sparsely researched. This paper aims to check its value for herbal adulteration concerning plants with slimming as an indication. Moreover, it is among the first to exploit
[...] Read more.
Mass spectrometric (MS) fingerprinting coupled with chemometrics for the detection of plants in plant mixtures is sparsely researched. This paper aims to check its value for herbal adulteration concerning plants with slimming as an indication. Moreover, it is among the first to exploit the full three-dimensional dataset (i.e., time × intensity × mass) obtained with liquid chromatography hyphenated with MS for herbal fingerprinting purposes. The MS parameters were optimized to achieve highly specific fingerprints. Trituration’s (total 55), blanks (total 11) and reference plants were injected in the MS system to generate the dataset. The dataset was complex and humongous, necessitating the application of compression techniques. After compression, Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) was performed to generate models validated for accuracy using cross-validation and an external test set. Confusion matrices were constructed to provide insight into the modeling predictions. A complimentary evaluation between data obtained using a previously developed Diode Array Detection (DAD) method and the MS data was performed by data fusion techniques and newly generated models. The fused dataset models were comparable to MS models. For ease of application, MS modeling was deemed to be superior. The future market studies would adopt MS modeling as the preferred choice. A proof of concept was carried out on 10 real-life samples obtained from illegal sources. The results indicated the need for stronger monitoring of (illegal) plant food supplements entering the market, especially via the internet.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Analytical Chemistry in Europe: Towards Sustainability and Quality of Life, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Studies on the Emission of Volatile Organic Compounds from Selected Forest Mushrooms of the Genus Lactarius Using Proton-Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometry
by
Tomasz Wróblewski, Anna Kamińska and Agnieszka Włodarkiewicz
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 3000; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30143000 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Forest mushrooms, due to their taste and smell, have been a component of people’s diets since the beginning of time. Unfortunately, there are many inedible or poisonous species of mushrooms that are similar to those that are eaten. For example, the highly valued
[...] Read more.
Forest mushrooms, due to their taste and smell, have been a component of people’s diets since the beginning of time. Unfortunately, there are many inedible or poisonous species of mushrooms that are similar to those that are eaten. For example, the highly valued Boletus edulis is similar to the inedible bitter bolete and the poisonous bolete. In the case of mushrooms of the genus Lactarius, such similarities are demonstrated by the delicious tasting L. deliciosus, the inedible downy L. pubescens and the poisonous cottony L. torminosus. This study presents an attempt to classify these three species based on studies of the emission of volatile organic compounds from the volatile headspace using proton-transfer reaction mass spectrometry (PTR-MS). The conducted statistical tests, principal component analysis (PCA) and discriminant analysis revealed significant differences in the concentration of 20 selected protonated VOC molecules for the tested mushroom species. The clear advantages of the PTR-MS technique are that there is no need for special sample preparation and it has rapid measurement capability and high analytical sensitivity. This allows for a quick comparative analysis of VOCs, for example, from different species of forest mushrooms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Direct Injection Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Food Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
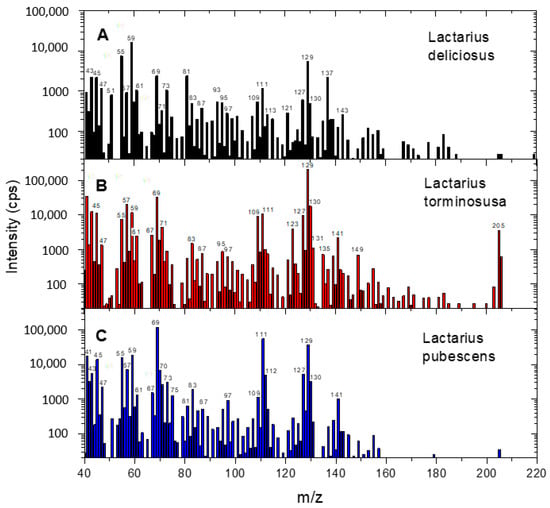
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mechanistic Study of Oil Adsorption Behavior and CO2 Displacement Mechanism Under Different pH Conditions
by
Xinwang Song, Yang Guo, Yanchang Chen and Shiling Yuan
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2999; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142999 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) via CO2 flooding is a promising strategy for improving hydrocarbon recovery and carbon sequestration, yet the influence of pH on solid–liquid interfacial interactions in quartz-dominated reservoirs remains poorly understood. This study employs molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to investigate
[...] Read more.
Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) via CO2 flooding is a promising strategy for improving hydrocarbon recovery and carbon sequestration, yet the influence of pH on solid–liquid interfacial interactions in quartz-dominated reservoirs remains poorly understood. This study employs molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to investigate the pH-dependent adsorption behavior of crude oil components on quartz surfaces and its impact on CO2 displacement mechanisms. Three quartz surface models with varying ionization degrees (0%, 9%, 18%, corresponding to pH 2–4, 5–7, and 7–9) were constructed to simulate different pH environments. The MD results reveal that aromatic hydrocarbons exhibit significantly stronger adsorption on quartz surfaces at high pH, with their maximum adsorption peak increasing from 398 kg/m3 (pH 2–4) to 778 kg/m3 (pH 7–9), while their alkane adsorption peaks decrease from 764 kg/m3 to 460 kg/m3. This pH-dependent behavior is attributed to enhanced cation–π interactions that are facilitated by Na+ ion aggregation on negatively charged quartz surfaces at high pH, which form stable tetrahedral configurations with aromatic molecules and surface oxygen ions. During CO2 displacement, an adsorption–stripping–displacement mechanism was observed: CO2 first forms an adsorption layer on the quartz surface, then penetrates the oil phase to induce the detachment of crude oil components, which are subsequently displaced by pressure. Although high pH enhances the Na+-mediated weakening of oil-surface interactions, which leads to a 37% higher diffusion coefficient (8.5 × 10−5 cm2/s vs. 6.2 × 10−5 cm2/s at low pH), the tighter packing of aromatic molecules at high pH slows down the displacement rate. This study provides molecular-level insights into pH-regulated adsorption and CO2 displacement processes, highlighting the critical role of the surface charge and cation–π interactions in optimizing CO2-EOR strategies for quartz-rich reservoirs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Molecular Modeling in Chemistry, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
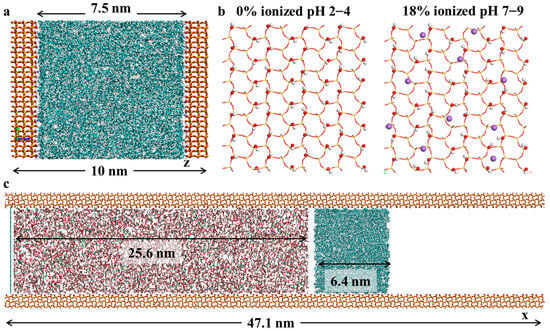
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Decoding the Architecture of Molecular Diodes: Rational Design for Ideal Rectification
by
Sara Gil-Guerrero, Nicolás Ramos-Berdullas and Marcos Mandado
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2998; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142998 - 17 Jul 2025
Abstract
The design of nanoscale electronic components remains a major challenge because we have limited control over the chemical and physical properties of their molecular constituents. Even subtle structural or compositional modifications can significantly alter their electronic behavior. Consequently, updating a molecular component often
[...] Read more.
The design of nanoscale electronic components remains a major challenge because we have limited control over the chemical and physical properties of their molecular constituents. Even subtle structural or compositional modifications can significantly alter their electronic behavior. Consequently, updating a molecular component often necessitates developing a new model from scratch. In this study, we present a comprehensive analysis of the rectification properties of a promising molecular diode initially proposed by Aviram and Van Dyck. The model has been systematically decomposed into fundamental building blocks, enabling the electron transport process to be examined both as an integrated event and as a sum of cooperative interactions. Our findings reveal that certain motifs—such as the D-σ-A architecture—play a significant role in rectification. However, achieving high-performance molecular rectifiers also requires cooperative interplay with other structural elements that contribute to rectification, such as asymmetric molecule–metal contacts. In this study, we conduct a detailed investigation of the roles these elements play in shaping the rectifying characteristics, and we further interpret their effects by analyzing the dominant transport channels under forward and backward bias conditions. This deeper understanding of the transport mechanism offers greater control over the system and opens the door for rational design strategies for improving rectification efficiency in future molecular devices.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exclusive Feature Papers in Physical Chemistry, 3nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
New Insights into Polymeric Liquid Crystals and Their Applications
by
A. C. Trindade, J. P. Canejo and P. L. Almeida
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2997; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142997 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Polymeric liquid crystals (PLCs) have emerged as one of the most frenetic and interdisciplinary areas of materials science, found at the crossroads of soft condensed matter, chemistry, physics, and engineering [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Polymeric Liquid Crystals and Applications)
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis of Anti-Inflammatory Flavones in Chrysanthemum indicum Capitula Using Primary Cultured Rat Hepatocytes
by
Keita Minamisaka, Airi Fujii, Cheng Li, Yuto Nishidono, Saki Shirako, Teruhisa Kawamura, Yukinobu Ikeya and Mikio Nishizawa
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2996; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142996 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
The capitula of Chrysanthemum indicum Linné or C. morifolium Ramatuelle (Kikuka in Japanese) are included in several formulae of Kampo medicines (traditional Japanese medicines), such as Chotosan, which is used for headache and dizziness. Luteolin, the principal constituent of C. indicum
[...] Read more.
The capitula of Chrysanthemum indicum Linné or C. morifolium Ramatuelle (Kikuka in Japanese) are included in several formulae of Kampo medicines (traditional Japanese medicines), such as Chotosan, which is used for headache and dizziness. Luteolin, the principal constituent of C. indicum, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, the effects of other flavonoids on this crude drug have not yet been thoroughly investigated. To evaluate and compare anti-inflammatory effects, we used primary cultured rat hepatocytes, which produce proinflammatory mediators, such as nitric oxide (NO) and proinflammatory cytokines, in response to interleukin (IL)-1β. Eight derivatives of 5,7-dihydroxyflavone were purified and identified in the ethyl acetate-soluble fraction of a C. indicum capitulum extract: luteolin (Compound 1), apigenin (2), diosmetin (3), 5,7-dihydroxy-3′,4′,5′-trimethoxyflavone (4), acacetin (5), eupatilin (6), jaceosidin (7), and 6-methoxytricin (8). Luteolin is the most abundant compound in this fraction. All compounds significantly suppressed NO production in hepatocytes, with apigenin and acacetin showing the greatest efficacy. The comparison of the IC50 values of the inhibition of NO production suggests that substitutions by hydroxyl and methoxy groups at the C-3′ and C-4′ positions of 5,7-dihydroxyflavone may be at least essential for the suppression of NO production. In hepatocytes, acacetin and luteolin decreased the levels of mRNAs encoding inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor, IL-6, and type 1 IL-1 receptor, which regulates inflammatory responses. Based on the comparison of the IC50 values and the content, luteolin, jaceosidin, and diosmetin may be responsible for the anti-inflammatory effects of C. indicum capitula.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Bioactive Compounds from Traditional Asian Plants—Second Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
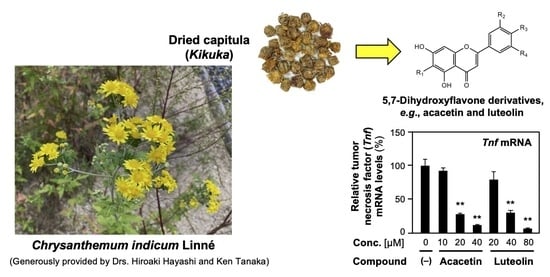
Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Development and Validation of a Highly Sensitive LC–MS/MS Method for the Precise Quantification of Sitagliptin in Human Plasma and Its Application to Pharmacokinetic Study
by
Yuna Song, Wang-Seob Shim, Eunseo Song, Yebeen Park, Bo-Hyung Kim, Sangmin Lee, Eun Kyoung Chung and Kyung-Tae Lee
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2995; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142995 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Sitagliptin is an orally bioavailable selective DPP4 inhibitor that reduces blood glucose levels without significant increases in hypoglycemia. The aim of this study was to design and validate an innovative, rapid, and highly sensitive LC–MS/MS assay for the precise measurement of sitagliptin concentrations
[...] Read more.
Sitagliptin is an orally bioavailable selective DPP4 inhibitor that reduces blood glucose levels without significant increases in hypoglycemia. The aim of this study was to design and validate an innovative, rapid, and highly sensitive LC–MS/MS assay for the precise measurement of sitagliptin concentrations in human plasma. This analytical method, utilizing sitagliptin-d4 as the internal standard, is performed using only 100 μL of plasma and a liquid–liquid extraction procedure based on methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE). Chromatographic separation is expertly achieved with a Kinetex® C18 column under isocratic elution, employing a perfect 1:1 blend of 5 mM ammonium acetate (with 0.04% formic acid) and acetonitrile, and maintaining an efficient flow rate of 0.2 mL/min. Detection occurs in positive ionization mode through multiple reaction monitoring, precisely targeting transitions of m/z 408.2 → 193.0 for sitagliptin and 412.2 → 239.1 for the IS. The total runtime of this assay is under 2 min. Comprehensive validation in line with MFDS and FDA criteria demonstrates outstanding linearity (5–1000 ng/mL, r2 > 0.998), alongside impressive levels of accuracy, precision, recovery and sample stability. Due to its minimal sample requirement and high-throughput capability, the validated approach is highly appropriate for pharmacokinetic and bioequivalence assessments involving sitagliptin.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Application of LC-MS in Pharmaceutical Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures
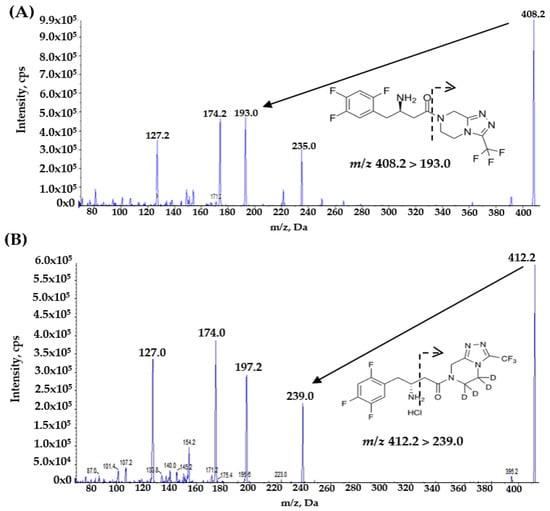
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Characteristics of the Content and Variability of Dietary Fiber Components and Alkylresorcinols of Rye Grain (Secale cereale L.)
by
Anna Fraś, Magdalena Wiśniewska, Dariusz R. Mańkowski and Marlena Gzowska
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2994; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142994 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Rye (Secale cereale L.) is one of the most important cereals cultivated in Central and Eastern Europe, valued for its high resistance to environmental stress and high levels of bioactive compounds, such as dietary fiber (DF) and alkylresorcinols (ARR). The aim of
[...] Read more.
Rye (Secale cereale L.) is one of the most important cereals cultivated in Central and Eastern Europe, valued for its high resistance to environmental stress and high levels of bioactive compounds, such as dietary fiber (DF) and alkylresorcinols (ARR). The aim of the study was to evaluate the content and variability of DF fractions and ARR in rye grain of hybrid and population cultivars. The research was conducted on grain from four rye cultivars cultivated in five locations over three consecutive growing seasons. The content of DF, its fractions, and ARR, was determined using enzymatic–gravimetric and colorimetric methods. The results showed significant variability in all analyzed traits, with environmental conditions and G×E interaction having the greatest impact on their content. Hybrid cultivars were characterized by a higher and more stable content of bioactive compounds. Notable average values for hybrids vs. populations included DF: 153.9 vs. 151.7 g kg−1, NSP: 129.4 vs. 127.7 g kg−1, lignin: 24.5 vs. 24.0 g kg−1, β-glucan: 21.7 vs. 20.6 g kg−1, and ARR: 1015 vs. 987 g kg−1. The KWS Serafino cultivar characterized by the highest and most stable content of bioactive compounds. Selecting genotypes with stable chemical profiles regardless of environmental conditions is crucial for developing nutritionally valuable rye-based products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Analysis and Biological Evaluation of Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
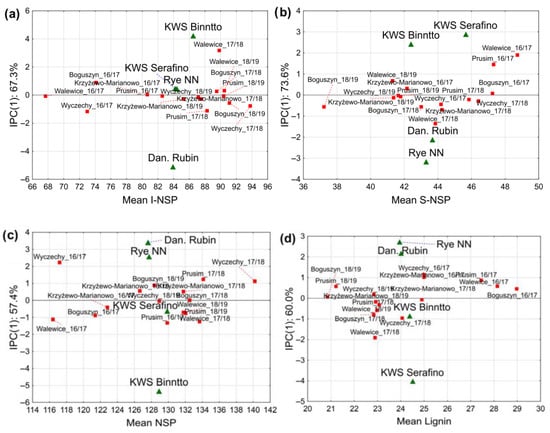
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Discovery of Species-Specific Peptide Markers for Superseed Authentication Using Targeted LC-MS/MS Proteomics
by
Sorel Tchewonpi Sagu, Beatrice Schnepf, Peter Stenzel, Kapil Nichani, Alexander Erban, Joachim Kopka, Harshadrai M. Rawel and Andrea Henze
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2993; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142993 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
The increasing popularity of “superseeds” such as flax, sesame, amaranth and quinoa as functional foods raises the need for robust analytical methods for authentication purposes. In this work, a standardized workflow for the extraction, characterization and identification of unique peptides that may be
[...] Read more.
The increasing popularity of “superseeds” such as flax, sesame, amaranth and quinoa as functional foods raises the need for robust analytical methods for authentication purposes. In this work, a standardized workflow for the extraction, characterization and identification of unique peptides that may be used as markers to distinguish superseed species was investigated. Ammonium bicarbonate/urea (Ambi/urea) extraction, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) buffer and trichloroacetic acid (TCA) precipitation were initially implemented and, based on the level and composition of the extracted proteins, the SDS buffer protocol was selected. Electrophoresis analysis revealed consistent protein profiles between biological replicates from each of the eleven seed species, confirming the reproducibility of the SDS buffer protocol. Targeted mass spectrometry successfully identified species-specific peptide markers for six of eleven superseeds investigated, including peptides from conlinins in flaxseed (WVQQAK), 11S globulins in sesame (LVYIER), oleosin in quinoa (DVGQTIESK), agglutin-like lectins in amaranth (CAGVSVIR), as well as cupin-like proteins in poppy seeds (INIVNSQK) and edestins in hemp seeds (FLQLSAER). Moreover, proteome cross-analysis allowed us to disqualify the isomeric peptide LTALEPTNR from 11S globulins present in amaranth and quinoa. However, no reliable markers were identified for chia, canihua, basil, black cumin, and psyllium seeds under current conditions. While this targeted proteomics approach shows promise for superseed authentication, comprehensive method validation and alternative strategies for marker-deficient species are required before routine implementation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Analytical Chemistry in Food Science)
►▼
Show Figures
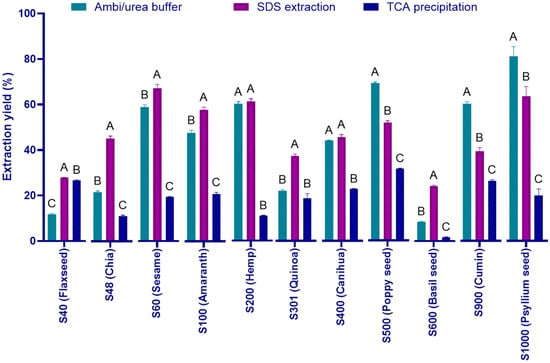
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Selective Cleaning Enhances Machine Learning Accuracy for Drug Repurposing: Multiscale Discovery of MDM2 Inhibitors
by
Mohammad Firdaus Akmal and Ming Wah Wong
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2992; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142992 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Cancer remains one of the most formidable challenges to human health; hence, developing effective treatments is critical for saving lives. An important strategy involves reactivating tumor suppressor genes, particularly p53, by targeting their negative regulator MDM2, which is essential in promoting cell cycle
[...] Read more.
Cancer remains one of the most formidable challenges to human health; hence, developing effective treatments is critical for saving lives. An important strategy involves reactivating tumor suppressor genes, particularly p53, by targeting their negative regulator MDM2, which is essential in promoting cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Leveraging a drug repurposing approach, we screened over 24,000 clinically tested molecules to identify new MDM2 inhibitors. A key innovation of this work is the development and application of a selective cleaning algorithm that systematically filters assay data to mitigate noise and inconsistencies inherent in large-scale bioactivity datasets. This approach significantly improved the predictive accuracy of our machine learning model for pIC50 values, reducing RMSE by 21.6% and achieving state-of-the-art performance (R2 = 0.87)—a substantial improvement over standard data preprocessing pipelines. The optimized model was integrated with structure-based virtual screening via molecular docking to prioritize repurposing candidate compounds. We identified two clinical CB1 antagonists, MePPEP and otenabant, and the statin drug atorvastatin as promising repurposing candidates based on their high predicted potency and binding affinity toward MDM2. Interactions with the related proteins MDM4 and BCL2 suggest these compounds may enhance p53 restoration through multi-target mechanisms. Quantum mechanical (ONIOM) optimizations and molecular dynamics simulations confirmed the stability and favorable interaction profiles of the selected protein–ligand complexes, resembling that of navtemadlin, a known MDM2 inhibitor. This multiscale, accuracy-boosted workflow introduces a novel data-curation strategy that substantially enhances AI model performance and enables efficient drug repurposing against challenging cancer targets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational and Theoretical Chemistry)
Open AccessArticle
Ligands of Biological and Environmental Interest as Sequestering Agents for Fe3+ in Aqueous Solution: A Speciation Study of Natural Fluids
by
Anna Irto, Ileana Ielo, Clemente Bretti, Francesco Crea, Concetta De Stefano and Rosalia Maria Cigala
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2991; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142991 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
The interactions of Fe3+ with some ligands (Tranexamic (TXA−), Indole-3-acetic (IAA−), and Aminomethylphosphonic (AMPA2−) acids) of biological and environmental interest were studied. The speciation studies were performed in NaNO3(aq) and NaCl(aq)
[...] Read more.
The interactions of Fe3+ with some ligands (Tranexamic (TXA−), Indole-3-acetic (IAA−), and Aminomethylphosphonic (AMPA2−) acids) of biological and environmental interest were studied. The speciation studies were performed in NaNO3(aq) and NaCl(aq) using potentiometric and, only for IAA−, spectrophotometric titrations at T = 298.15 K and 0.01 ≤ I/mol dm−3 ≤ 1.0. The proposed speciation models are as follows: Fe(TXA)H3+, Fe(TXA)2+, Fe(TXA)(OH)+, and Fe(TXA)(OH)2(aq) for TXA−; Fe(IAA)2+ for IAA−; and Fe(AMPA)H23+, Fe(AMPA)H2+, and Fe(AMPA)+ for AMPA2−. A comparison of logβ for the common FeL species gives logβFeIAA = 6.56 and logβFeAMPA = 14.84 (at I = 1.00 mol dm−3 and T = 298.15 K), suggesting that AMPA2− has a higher complexing ability towards Fe3+ than IAA−. The dependence on the ionic strength of the formation constants was modeled by means of a Debye–Hückel type equation and the SIT model, whilst the sequestering ability of the investigated ligands towards Fe3+ was quantified at various pHs, ionic strengths, and in the different supporting electrolytes by means of an empirical pL0.5 parameter. To complete this study of the behavior of the different Fe3+/ligand systems, various simulations in biological fluids and natural waters were conducted.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Analytical Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Ultraporous Amine-Functionalized Organosilicas: Tuning Morphology and Surface Chemistry for Adsorption Applications
by
Marlena Bytniewska, Kacper Latusek, Maria Powęzka, Marcin Kuśmierz, Oliwia Kapusta and Mariusz Barczak
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2990; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142990 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Highly porous organosilicas were synthesized via direct co-condensation of two monomers, bis (triethoxysilyl) benzene and aminopropyltriethoxysilane, by adjusting the time between consecutive additions of the monomers and the ageing time of the as-obtained samples. The resulting organosilicas exhibited high porosities, with total pore
[...] Read more.
Highly porous organosilicas were synthesized via direct co-condensation of two monomers, bis (triethoxysilyl) benzene and aminopropyltriethoxysilane, by adjusting the time between consecutive additions of the monomers and the ageing time of the as-obtained samples. The resulting organosilicas exhibited high porosities, with total pore volumes exceeding 2.2 cm3/g. Alongside detailed insights into the morphology, structure, and surface chemistry via a broad spectrum of various instrumental techniques, the obtained ultraporous amine-functionalized organosilicas were tested as adsorbents of diclofenac sodium, chosen here as a model drug. The results revealed remarkable differences in the physicochemical properties and adsorption efficiencies among the obtained samples, confirming that the time gap between the addition of the monomers and ageing time can be used to tune the morphological, structural, and chemical features of the obtained organosilicas and, as a consequence, their sorption efficiencies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design and Synthesis of Novel Adsorbents for Pollutant Removal, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Compositional Variability of Essential Oils and Their Bioactivity in Native and Invasive Erigeron Species
by
Asta Judžentienė
Molecules 2025, 30(14), 2989; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30142989 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
To date, various species of Erigeron genus have been used both in the ethnopharmacology of numerous nations across the world and in contemporary herbal practices. The objective of this study is to revise the phytochemical data on the essential oils (EOs) of various
[...] Read more.
To date, various species of Erigeron genus have been used both in the ethnopharmacology of numerous nations across the world and in contemporary herbal practices. The objective of this study is to revise the phytochemical data on the essential oils (EOs) of various fleabanes species and to evaluate the variability of their biological activities. Up to June 2025, this review provides an updated overview of 105 literature sources (published during last 25 years) related to 14 Erigeron sp. (native, naturalized, or invasive) which have been investigated extensively and are of the greatest significance. It summarizes the compositional variability of the EOs and their pharmacological and toxic effects, such as anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antiproliferative, skin regeneration, antioxidant, antifungal, antibacterial, insecticidal, larvicidal, repellent, and allelopathic activity. The EOs of each Erigeron species were characterized, and a chemical structure of 43 major constituents is presented herein. The most characteristic and prevalent compounds were found to be limonene, δ-3-carene, matricaria ester, lachnophyllum ester, germacrene D, β-caryophyllene, β-farnesene, α-bergamotene, allo-aromadendrene, etc., in the EOs from the E. acris, E. annuus, E. bonariensis, E. canadensis, E. floribundus E. mucronatus, and E. speciosus plants. Major constituents, such as borneol, bornyl acetate, modhephen-8-β-ol, cis-arteannuic alcohol, β-caryophyllene, and τ-cadinol, were found in the oils of E. graveolens (Inula graveolens). A paucity of data concerning E. incanus EOs was revealed, with the prevalence of 3-hydroxy-4-methoxy cinammic acid and thymol acetate noted in the oils. The EOs from E. multiradiatus and E. sublyratus were comprised mainly of matricaria and lachnophyllum esters. The available data on EOs of E. ramosus is limited, but the main constituents are known to be α-humulene, 1,8-cineole, eugenol, and globulol. The EOs containing appreciable amounts of matricaria and lachnophyllum esters exhibited strong anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, larvicidal, and repellent activities. Repellence is also related to borneol, bornyl acetate, caryophyllene derivatives, τ-cadinol, modhephen-8-β-ol, and cis-arteannuic alcohol. Cytotoxicity was determined due to the presence of limonene, δ-3-carene, α- and β-farnesene, (E)-β-ocimene, ledene oxide, sesquiphellandrene, and dendrolasin in the fleabanes EOs. Skin regeneration and antifungal properties were related to germacrene D; and anti-inflammatory effects were determined due to high amounts of limonene (E)-β-ocimene, lachnophyllum ester, and germacrene D. The antimicrobial properties of the oils were conditioned by appreciable quantities of limonene, β-pinene, 1,8-cineole, carvacrol, thymol acetae, β-eudesmol, 2,6,7,7α-tetrahydro-1,5-dimethyl-1H-indene-3-carboxaldehyde, caryophyllene and its oxide, allo-aromadendrene, α-humulene, farnesene, carvacrol, and eugenol. This review provides a foundation for further studies on volatile secondary metabolites to explore the potential sources of new biologically active compounds in Erigeron sp.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Featured Reviews in Natural Products Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Molecules Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Vol. 30 (2025)
- Vol. 29 (2024)
- Vol. 28 (2023)
- Vol. 27 (2022)
- Vol. 26 (2021)
- Vol. 25 (2020)
- Vol. 24 (2019)
- Vol. 23 (2018)
- Vol. 22 (2017)
- Vol. 21 (2016)
- Vol. 20 (2015)
- Vol. 19 (2014)
- Vol. 18 (2013)
- Vol. 17 (2012)
- Vol. 16 (2011)
- Vol. 15 (2010)
- Vol. 14 (2009)
- Vol. 13 (2008)
- Vol. 12 (2007)
- Vol. 11 (2006)
- Vol. 10 (2005)
- Vol. 9 (2004)
- Vol. 8 (2003)
- Vol. 7 (2002)
- Vol. 6 (2001)
- Vol. 5 (2000)
- Vol. 4 (1999)
- Vol. 3 (1998)
- Vol. 2 (1997)
- Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Electrochem, IJMS, Molecules, Polymers, Separations
Advances in Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Cristina Orbeci, Cristian Pirvu, Ileana Rau, Stefania Stoleriu, Maria-Cristina Todasca, Elena Iuliana BîruDeadline: 31 July 2025
Topic in
Analytica, Molecules, Nanomaterials, Polymers, Magnetochemistry, Biosensors
Nanomaterials in Green Analytical Chemistry
Topic Editors: George Zachariadis, Rosa Peñalver, Natalia ManousiDeadline: 15 August 2025
Topic in
Energies, Materials, Molecules, Waste, Water, Sustainability
Advances in Organic Solid Waste and Wastewater Management
Topic Editors: Alejandro Alvarado-Lassman, Carlos Velasco-Santos, Juan Manuel Méndez-ContrerasDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topic in
Biomolecules, IJMS, Molecules, Sci. Pharm., Marine Drugs, Plants
Antioxidant Activity of Natural Products—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: José Virgílio Santulhão Pinela, Maria Inês Moreira Figueiredo Dias, Carla Susana Correia Pereira, Alexandra PlácidoDeadline: 30 September 2025

Conferences
26–29 August 2025
The 5th International Symposium on Frontiers in Molecular Science
Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms of Biological Function and Drug Discovery based on Protein Structure/Function Analysis
Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms of Biological Function and Drug Discovery based on Protein Structure/Function Analysis

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Molecules
Lipids and Surfactants in Delivery Systems
Guest Editors: Agnieszka Lewińska, Marta Domżał-KędziaDeadline: 22 July 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
Unlocking the Formulation Potential of Cyclodextrins and Their Derivatives—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Georgia N. Valsami, Natassa Pippa, Paraskevi PapakyriakopoulouDeadline: 25 July 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
Surfactants at the Soft Interfacial Layer
Guest Editor: Chi PhanDeadline: 31 July 2025
Special Issue in
Molecules
The Medicinal Value of Natural Products
Guest Editor: Leticia M. EstevinhoDeadline: 31 July 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Antibiotics & Superbugs: New Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
Collection Editor: Peter J. Rutledge
Topical Collection in
Molecules
Preanalytical Methods for Natural Products Production
Collection Editors: Young Hae Choi, Farid Chemat, Giancarlo Cravotto, Erica G. Wilson









